| Near Eastern religion | Eastern religion |
| Truth is singular and hierarchical, focussed and guaranteed in the Godhead. The material has a real basis of existence. Material and spiritual fact is stronger than story, and story points to fact, in the ultimate. | Truth is pluriform and many, ultimately to be dispersed and illusory except for the place where material reality is not to be. Story is stronger than fact, and fact always becomes a story, in the ultimate, because the ultimate is without form. |
| Time is linear because everyone is involved collectively and individual experience falls within the history of everyone. | Time is cyclical because individual experience is all, and everyone through time repeats what others have done. |
| A Creator God who has an intervention into history personality at the highest level. | Ultimate Reality is undifferentiated and impersonal and personality characteristics are at a lower level. |
| The human is different from God and the soul needs saving, if soul there is, or the body dies and waits to rise at the end of earthly time | The body is a surface appearance of the soul that is real, and which is developed while in a body to become one with God (Atman with Brahman). Or the self is to be extinguished so to become no more a craving and no longer contrasted with the pure selfless state of Nirvana. |
| Evil is a condition of sinning against the perfection of God which needs acceptance of God and God to redeem. | Evil is from suffering and part of delusion and requires stage by stage improvement towards perfection. |
| Salvation depends on following the law, faith or good works and hell or abandonment from God is to be resisted in favour of heaven or resurrection into paradise. | Salvation is about following the way towards improvement through wisdom and knowledge for he perfect vision as at the ultimate stage. Doing this puts to an end the experience of suffering and therefore a state of blissfulness. |
| Spiritual access is ultimately democratic (although priesthoods developed) where any or all can be saved. | Spiritual access is ultimately hierarchical where successive progress means some are higher up the enlightenment ladder than others. |
| Prayer may petition God but all prayer and worship is sacrificial, or highly dutiful, with much ritual or form. | The means to improvement is meditation and changing consciousness towards wisdom. |
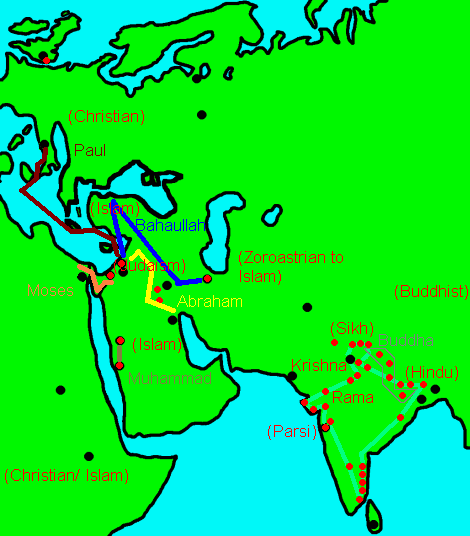
Nevertheless there are overlaps and one of the largest is in panentheism. Some Eastern religions tend towards pantheism or atheism, but have tendencies which emphasise God with characteristics, whereas Near Eastern religions which emphasise God have certain spiritual tendencies which go towards pantheism. Also all religions at a popular level have tendencies towards if not fully worked out polytheism and magical religion. Non-Near Eastern religions explore devas, deities and the supernatural more (including no-God Buddhism!) than religions which emphasise one God.
Furthermore some faiths which are closer to the centre of these two spans. Sikhism has a Sufi Islam and Hindu origin and so combines aspects of progressive revelation and linear time into non-linear elements, and Bahai theology includes aspects of plurality and relativity within an overall time-historical scheme. Zoroastrianism, a linear faith, nevertheless gave influence to Gnosticism with is similarity to Eastern forms of spirit-material hierarchy. There is also a third more humanistic or rationalised alternative, in pregressive liberal religion that features in all faiths whether Christian Unitarianism or Hindu Brahmo Samaj.
| 1300 B.C.E. | Vedas developing (Rig Veda, Yajur Veda, Sama Veda, Atharva Veda) |
| 900 | |
| 1250 | Moses & Exodus |
| 1100 | Zoroaster |
| 600 | Upanishads written |
| 300 | |
| 563 | Life of Buddha |
| 483 | |
| 586 | Destruction of First Temple and Babylonian captivity of the Judeans |
| 527 | Vardhamana Mahvira, last sage of Jainism, dies |
| 400 B.C.E. | Mahabharata compiled |
| 300 C.E. | |
| 260 B.C.E. | Conversion of King Ashoka to Buddhism |
| 200 B.C.E. | Ramayana compiled |
| 200 C.E. | |
| 100 | Mahayana Buddhism emerges |
| 4 B.C.E. | Life of Jesus of Nazareth |
| 30 C.E. | |
| 70 | Destruction of Second Temple |
| 90 | Council of Jamnia fixes Jewish canon |
| 250 | Death of Nagarjuna |
| 367 | Athanasius lists books of the New Testament canon |
| 570 | Life of Muhammad |
| 632 | |
| 651 | Caliph Uthman's united version of the Qur'an completed |
| 700 | Early Hindu Tantras |
| 750 | Start of Abbasid Caliphate |
| 788 | Life of Shankara (founder of Advaita Vedanta, non-duality school) |
| 820 | |
| 1054 | Division of Roman Catholic and Orthodox Churches |
| 1400 | Rig Veda in writing complete and collected |
| 1440 | Life of Kabir (Hindu-Muslim mystic) |
| 1518 | |
| 1469 | Life of Guru Nanak |
| 1539 | |
| 1517 | Start of the Protestant Reformation |
| 1666 | Life of Guru Gobind Singh |
| 1708 | |
| 1708 | Guru Gobind Singh makes Adi Granth become Guru Granth Sahib |
| 1772 | Life of Ram Mohan Roy |
| 1833 | |
| 1828 | Brahmo Samaj founded (by Ram Mohan Roy) |
| 1817 | Life of Baha’u’llah |
| 1892 | |
| 1836 | Life of Ramakrishna |
| 1886 | |
| 1863 | Life of Vivikenanda |
| 1902 | |
| 1869 | Life of Mohandas K. Gandhi |
| 1948 | |
| 1893 | World Parliament of Religions, Chicago, United States |
| 1897 | Ramakrishna Mission founded (by Vivikenanda) |

Adrian Worsfold
A number of ideas (especially the timeline) and the basis for the map from:
Momen, M (1999), The Phenomenon of Religion: A Thematic Approach, Oxford: One World.