
A Virus enters the body as a result of environmental contact.

 When the Virus has entered the body and seeks out cells in which to reproduce, Macrophages detect the virus. The Macrophages can digest material external to the body and strip off the antibodies to stick on to themselves. It also demands T Helper cells come in and assist.
When the Virus has entered the body and seeks out cells in which to reproduce, Macrophages detect the virus. The Macrophages can digest material external to the body and strip off the antibodies to stick on to themselves. It also demands T Helper cells come in and assist.

There are several types of T cells. Just a small number of T Helper cells in the body are capable of reading the antibody and become activated and then go to the spleen and lymphatic glands to activate other cells. As the virus gets into host cells and starts to reproduce, T Cytotoxic cells come in and break the membranes of occupied cells to kill the whole cells and stop the reproduction. The T Suppressor cells are necessary to cut the activities of the T cytotoxic cells and also B cells once the invasion is defeated. There are also T Memory cells for future response.

|
|

|
|
 B cells in the spleen and lymphatic glands also respond to T Helper cells and produce Antibodies of Y shapes that directly stick to disease agent and stop these entering cells. There are B Memory cells too.
B cells in the spleen and lymphatic glands also respond to T Helper cells and produce Antibodies of Y shapes that directly stick to disease agent and stop these entering cells. There are B Memory cells too.
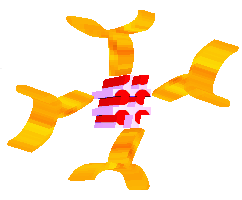
T Memory and B Memory cells remain in the blood and lymphatic system ready to fight the same virus should it enter the body again, and thus provides an immediate effective defence.
|
|
Adrian Worsfold
Idea from Yahya, H. (1999), The Signs in the Heavens and the Earth: For Men of Understanding, London: Ta-Ha Publishers. This book is an example of scientific detail attached to a viewpoint deliberately made to fit the Qur'an.